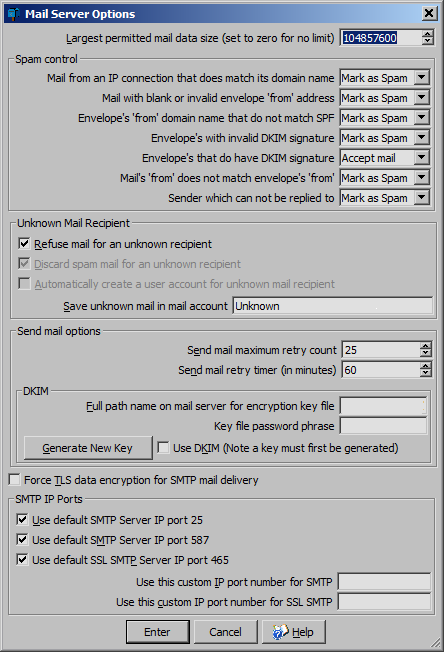
SMTP Server Options
The Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) server options are available from the menu Server > Server mail options. These are the options for receiving and sending email.
Force TLS data encryption for SMTP mail delivery
When receiving mail the connection can be encrypted. This is important if the mail connection is going over the WWW,which is normally the case and the mail contents contain sensitive data. This option will force all mail delivery to use TLS, which is a standardized encryption, when receiving mail. Otherwise the Mail Server will simply refuse the mail connection.
Largest permitted mail data size
This limits the largest mail data size. It works by telling the source this is the largest size mail the Mail Server will accept.
If this value is zero then there is no limit. By default this is set to 100MB.
Mail from an IP connection that does not match its domain name
When a sending mail client or Mail Transfer Agent (MTA) connects the IP address is known. SMTP protocol requires that the welcoming (HELO) message must contain the Full Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) or if that is not available then it must state its IP address. The IP addresses of the of the FQDN can be retrieved from Domain Name Servers (DNS) and the connecting IP address can be checked to see if it is one of them. If not the connection can be "refused", "accepted" or all delivered mail marked as "spam".
The default is to treat the mail as spam, as this implies the mail client or MTA is an imposter.
Mail with blank or invalid envelope 'from' address
Whenever mail is received with the 'From' field blank or invalid it can be "refused", "accepted" or marked as "spam".
The default is to treat the mail as spam, as an anonymous 'From:' is suspicious.
Envelope's 'from' domain name that do not match SPF
Envelope's 'from' domain name that do not match Senders Policy Framework (SPF). A mail server's DNS setting can be have text records that informs what hosts IP addresses are allowed to send mail for the domain. When receiving mail this information can be retrieved and the IP of the connecting mail client or MTA can be verified as being permitted to send mail for this domain. If this can not be verified then the received mail can be "refused", "accepted" or marked as "spam".
The default is to treat the mail as spam, as the send can not be verified.
Note that not all mail clients or MTA provide their SPF, in which case the mail can still be legitimate.
Envelope's has an invalid DKIM signature
Mail envelope's can contain a DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) signature. The purpose of this is to ensure that the mail has not been tampered with. If the mail is altered then the signature will not be valid. If it is invalid then the received mail can be "Refuse mail", "Accept mail" or "Marked as Spam".
The default is to treat the mail as spam. This is because the mail is often passed from one MTA to another and some systems alter the line length and make other alterations to space characters that the user would not normally see. This can make the signature invalid. Setting it to spam helps to alert the mail recipient to treat this mail with some suspicion.
Envelope's does not have a DKIM signature
Mail service providers and larger organisations would mark the envelope with a DKIM signature. This is to ensure that if the mail is tampered with the signature will become invalid. If it there is no signature then the received mail can be "Refuse mail", "Accept mail" or "Marked as Spam".
The default is to treat the mail as accepted. As there are still lots of smaller organisation that do not sign their out going mail.
Mail's 'from' does not match envelope's 'from'
When mail is sent by SMTP it has two 'from's. A hidden one referred to as on the envelope and also known as Return-Path, reverse-path, bounce address, mfrom, or envelope sender. As well as one in the header of the mail body, which the user sees and will reply to. When mail body 'from' does not match envelope 'from' then the received mail can be "Refuse mail", "Accept mail" or "Marked as Spam".
The default is to treat the mail as accept, because it is valid for these 'from's to be different. However setting it to spam helps to alert the mail recipient to treat this mail with some suspicion.
Sender which can not be replied to
It is normal to expect that mail can be replied to. When mail is received it is possible to contact the mail exchange for the sender and check if they are willing to accept mail for that address. Sender which can not be replied to can be "Refuse mail", "Accept mail" or "Marked as Spam".
Mail sent from a mailing list however do not always have a 'from' that can be replied to. So the default is to treat the mail as accept.However setting it to spam helps to alert the mail recipient to treat this mail with some suspicion and in any case mail sent from mail lists are normally junk mail anyway.
Automatically create a user account for unknown mail recipient
Whenever mail is received for an account that does not exist on the mail server then this option when enabled will automatically create a user account for it. This option can be useful when first setting up the Mail Server, however normally this option should be turned off
If this option in not enabled and the field "Save unknown mail in user account (blank to reject mail)" is left blank then the mail will just be rejected.
This option is not used if the "Refuse mail for unknown recipient" is enabled.
Save unknown mail in user account
Mail for a unknown mail recipient will sent to the specific account. This will only work if the Option "Automatically create a user account for unknown mail recipient" is not enabled. If the field is left blank then the mail will just be rejected.
This option is not used if the "Refuse mail for unknown recipient" is enabled or "automatically create a user account for unknown mail recipient" is enabled.
Send mail maximum retry count
Mail that is to be sent is copied into the Out Tray. Mail in the Out Tray will be delivered as soon as possible. If the receiving end is not working then the mail will remain in the Out Tray. Once the number of attempts to deliver the mail is reached then the mail will be destroyed and a notification mail will be sent to the sender. The time to wait before trying again is set in the "Send mail retry timer" field.
By default the number of retries is 24. With the "Send mail retry timer" field set to 60 minutes it will take up 24 hours before the mail maybe marked as undeliverable.
Send mail retry timer (in minutes)
This parameter works in conjunction with the above "Send mail Maximum retry count". It is the time between attempts to send the mail to the destined Server.
The value is in minutes. By default it is 60 minutes.
DKIM
Mail envelope's can contain a DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) signature. The purpose of this is to ensure that the mail has not been tampered with. If the mail is altered then the signature will not be valid. It is possible to set up the mail server to send its mail with a DKIM signature.
Full path name of mail server of encryption key file
This is where the generated encryption key file is stored on the mail server computer.
Generate new key button
A secure private key / public key pair are needed for the encryption of the hash codes. These keys are very large prime numbers. These are generated when this button is pressed Note that the larger the bit size of the number the more secure it is, however it will require more processing power and hence time to send the mail. Also the keys take much longer to generate if they are bigger.
Once the keys are generated a dialog box will appear with the (DNS) zone TXT record. This can be copied to the clip board or saved to a file. Using your DNS service provider this record will need to be added to the list of zones TXT records. You need to do this before selecting the use DKIM option. The private key / public key pair will be sent to the mail server and stored in the folder path name described. This file should be backed up and kept secure.
When generating the DKIM keys a selector label must be chosen. This is used by the receiving mail server to find the corresponding Domain Name Server (DNS) zone TXT record from your site. This TXT record has the public key that is used for encrypting the hash code used as the signature. For example the label "S123" could be used. It is ideal if the label contains a numerical part as it should be different whenever new keys are generated.
When generating the DKIM keys they can have a limited life set by the expiry period. Setting the value to zero will not set an expiry time for the keys. If an expiry time is set and it has expired then a new key with a new selector will need to be generated.
The generated record contains the public key, it needs to be copied and added to the sites DNS. If your selector is "s1" and your domain name is "emailer.net" then you will need to create a TXT record s1._domainkey.emailer.net and set the contents to the generated record.
Use DKIM option
Select this to active this functionality.
Force TLS data encryption for SMTP mail delivery
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) supports TLS data encryption. However it is up to the mail client or delivering mail server to decide to use encryption or not. With this flag set then mail transfer will not be allowed to occur if the delivering end did not use TLS. All normal mail clients and servers support TLS however simpler embedded device may not have this capability.
Outgoing mail exchange
Many internet service providers block outgoing IP port 25. They do this to try and stop spam sent from infected client computers. This means that mail can not be sent directly from mail servers that their clients run. To provide for this they expect that any clients that run a mail server to instead send their outgoing mail to their own mail exchange server. This server will forward the mail on. This server often has a name like mail.serviceprovider.com but can be different depending upon the providers choice. To use this the mail exchange name needs to be entered in the "Name of mail exchange server" field. This is often all that is required and all outgoing mail will be sent to this server using port 25. The mail exchange server will then deliver the mail. However some providers are more strict and will only send on mail from authorised users. For this extra fields are provided to enter a user name and password. In this case the mail will be sent to the mail exchange submission IP port 587.
Note when using this some of the other features that directly control how mail will be delivery become irrelevant and do not work.
Note that if the SPF record is set for the domain. It will need to be updated to include the providers SPF record. Otherwise delivered mail will be marked as spam. The updated SPF record will look something like the following.
v=spf1 a include:serviceprovider.com -all
SMTP IP Ports
These parameters allow control over the mail SMTP IP ports.
IP port 25 is the standard mail SMTP port. It is used to send and receive mails between mail servers.
IP port 587 is used to accept mail from mail clients, to then be forwarded on to the required destinations.
IP port 465 uses SSL encryption. It is used to accept mail from clients using with the data encrypted so the mail contents it can not be seen on the network. However as the other SNMP IP ports (25 & 587) can use TLS for encryption this IP port is not commonly used.
Alternatively a user chosen IP port number can be used by specifying a custom port number. Similarly a custom IP port can be picked for SSL communication.